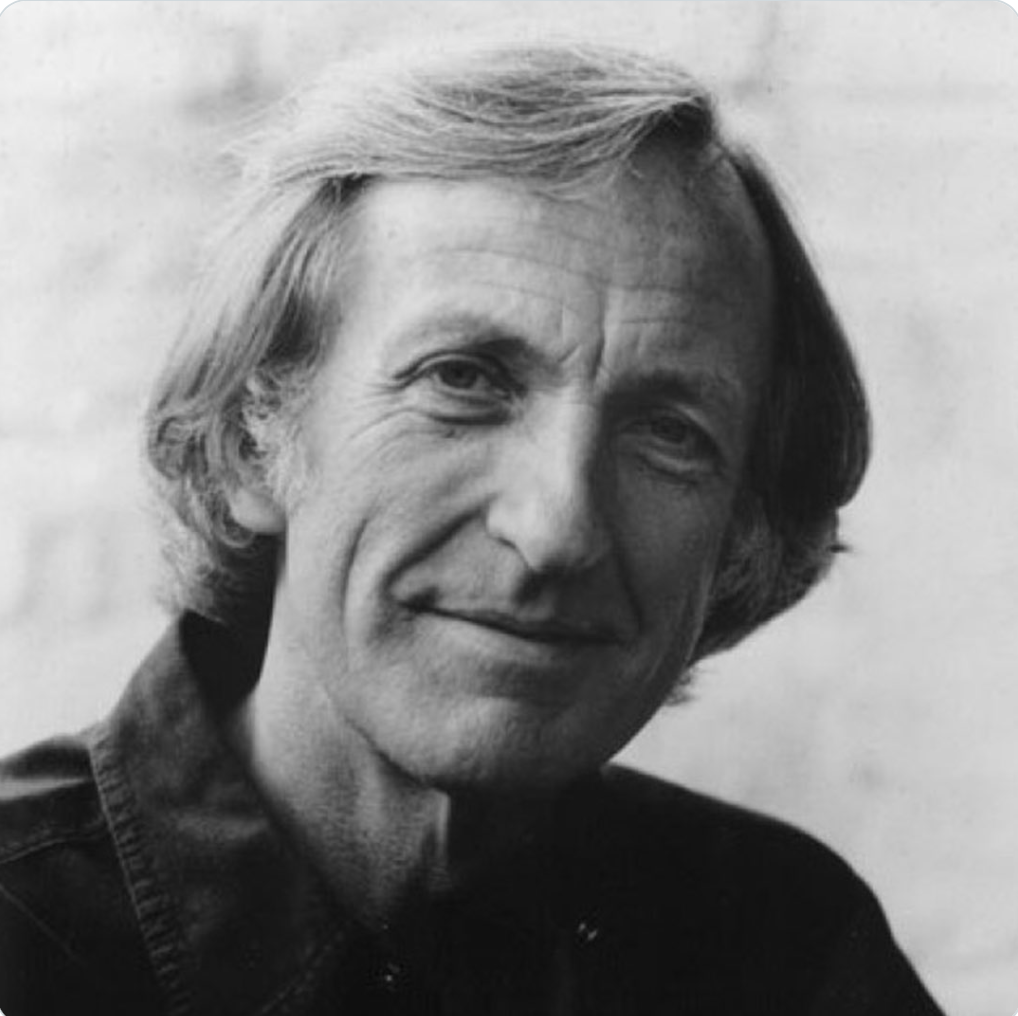
The High Court in London will soon to decide whether Julian Assange is to be extradited to Sweden to face allegations of sexual misconduct. At the appeal hearing in July, Ben Emmerson QC, counsel for the defence, described the whole saga as “crazy”. Sweden’s chief prosecutor had dismissed the original arrest warrant, saying there was no case for Assange to answer. Both the women involved said they had consented to have sex. On the facts alleged, no crime would have been committed in Britain.
However, it is not the Swedish judicial system that presents a “grave danger” to Assange, say his lawyers, but a legal device known as a Temporary Surrender, under which he can be sent on from Sweden to the United States secretly and quickly. The founder and editor of WikiLeaks, who published the greatest leak of official documents in history, providing a unique insight into rapacious wars and the lies told by governments, is likely to find himself in a hell hole not dissimilar to the “torturous” dungeon that held Private Bradley Manning, the alleged whistleblower. Manning has not been tried, let alone convicted, yet on 21 April, President Barack Obama declared him guilty with a dismissive “He broke the law”.
This Kafka-style justice awaits Assange whether or not Sweden decides to prosecute him. Last December, the Independent disclosed that the US and Sweden had already started talks on Assange’s extradition. At the same time, a secret grand jury – a relic of the 18th century long abandoned in this country – has convened just across the river from Washington, in a corner of Virginia that is home to the CIA and most of America’s national security establishment. The grand jury is a “fix”, a leading legal expert told me: reminiscent of the all-white juries in the South that convicted blacks by rote. A sealed indictment is believed to exist.
Under the US Constitution, which guarantees free speech, Assange should be protected, in theory. When he was running for president, Obama, himself a constitutional lawyer, said, “Whistleblowers are part of a healthy democracy and must be protected from reprisal”. His embrace of George W. Bush’s “war on terror” has changed all that. Obama has pursued more whistleblowers than any US president. The problem for his administration in “getting” Assange and crushing WikiLeaks is that military investigators have found no collusion or contact between him and Manning, reports NBC. There is no crime, so one has to be concocted, probably in line with Vice President Joe Biden’s absurd description of Assange as a “hi-tech terrorist”.
Should Assange win his High Court appeal in London, he could face extradition direct to the United States. In the past, US officials have synchronised extradition warrants with the conclusion of a pending case. Like its predatory military, American jurisdiction recognises few boundaries. As the suffering of Bradley Manning demonstrates, together with the recently executed Troy Davis and the forgotten inmates of Guantanamo, much of the US criminal justice system is corrupt if not lawless.
In a letter addressed to the Australian government, Britain’s most distinguished human rights lawyer, Gareth Peirce, who now acts for Assange, wrote, “Given the extent of the public discussion, frequently on the basis of entirely false assumptions… it is very hard to attempt to preserve for him any presumption of innocence. Mr. Assange has now hanging over him not one but two Damocles swords, of potential extradition to two different jurisdictions in turn for two different alleged crimes, neither of which are crimes in his own country, and that his personal safety has become at risk in circumstances that are highly politically charged.”
These facts, and the prospect of a grotesque miscarriage of justice, have been drowned in a vituperative campaign against the WikiLeaks founder. Deeply personal, petty, perfidious and inhuman attacks have been aimed at a man not charged with any crime yet held isolated, tagged and under house arrest – conditions not even meted out to a defendant presently facing extradition on a charge of murdering his wife.
Books have been published, movie deals struck and media careers launched or kick-started on the assumption that he is fair game and too poor to sue. People have made money, often big money, while WikiLeaks has struggled to survive. On 16 June, the publisher of Canongate Books, Jamie Byng, when asked by Assange for an assurance that the rumoured unauthorised publication of his autobiography was not true, said, “No, absolutely not. That is not the position … Julian, do not worry. My absolute number one desire is to publish a great book which you are happy with.” On 22 September, Canongate released what it called Assange’s “unauthorised autobiography” without the author’s permission or knowledge. It was a first draft of an incomplete, uncorrected manuscript. “They thought I was going to prison and that would have inconvenienced them,” he told me. “It’s as if I am now a commodity that presents an incentive to any opportunist.”
The editor of the Guardian, Alan Rusbridger, has called the WikiLeaks disclosures “one of the greatest journalistic scoops of the last 30 years”. Indeed, this is part of his current marketing promotion to justify raising the Guardian’s cover price. But the scoop belongs to Assange not the Guardian. Compare the paper’s attitude towards Assange with its bold support for the reporter threatened with prosecution under the Official Secrets Act for revealing the iniquities of Hackgate. Editorials and front pages have carried stirring messages of solidarity from even Murdoch’s Sunday Times. On 29 September, Carl Bernstein was flown to London to compare all this with his Watergate triumph. Alas, the iconic fellow was not entirely on message. “It’s important not to be unfair to Murdoch,” he said, because “he’s the most far seeing media entrepreneur of our time” who “put The Simpsons on air” and thereby “showed he could understand the information consumer”.
The contrast with the treatment of a genuine pioneer of a revolution in journalism, who dared take on rampant America, providing truth about how great power works, is telling. A drip-feed of hostility runs through the Guardian, making it difficult for readers to interpret the WikiLeaks phenomenon and to assume other than the worst about its founder. David Leigh, the Guardian’s “investigations editor”, told journalism students at City University that Assange was a “Frankenstein monster” who “didn’t use to wash very often” and was “quite deranged”. When a puzzled student asked why he said that, Leigh replied, “Because he doesn’t understand the parameters of conventional journalism. He and his circle have a profound contempt for what they call the mainstream media”. According to Leigh, these “parameters” were exemplified by Bill Keller when, as editor of the New York Times, he co-published the WikiLeaks disclosures with the Guardian. Keller, said Leigh, was “a seriously thoughtful person in journalism” who had to deal with “some sort of dirty, flaky hacker from Melbourne”.
Last November, the “seriously thoughtful” Keller boasted to the BBC that he had taken all WikiLeaks’ war logs to the White House so the government could approve and edit them. In the run-up to the Iraq war, the New York Times published a series of now notorious CIA-inspired claims claiming weapons of mass destruction existed. Such are the “parameters” that have made so many people cynical about the so-called mainstream media.
Leigh went as far as to mock the danger that, once extradited to America, Assange would end up wearing “an orange jump suit”. These were things “he and his lawyer are saying in order to feed his paranoia”. The “paranoia” is shared by the European Court of Human Rights which has frozen “national security” extraditions from the UK to the US because the extreme isolation and long sentences defendants can expect amounts to torture and inhuman treatment.
I asked Leigh why he and the Guardian had adopted a consistently hostile towards Assange since they had parted company. He replied, “Where you, tendentiously, claim to detect a ‘hostile toe’, others might merely see well-informed objectivity.”
It is difficult to find well-informed objectivity in the Guardian’s book on Assange, sold lucratively to Hollywood, in which Assange is described gratuitously as a “damaged personality” and “callous”. In the book, Leigh revealed the secret password Assange had given the paper. Designed to protect a digital file containing the US embassy cables, its disclosure set off a chain of events that led to the release of all the files. The Guardian denies “utterly” it was responsible for the release. What, then, was the point of publishing the password?
The Guardian’s Hackgate exposures were a journalistic tour de force; the Murdoch empire may disintegrate as a result. But, with or without Murdoch, a media consensus that echoes, from the BBC to the Sun, a corrupt political, war-mongering establishment. Assange’s crime has been to threaten this consensus: those who fix the “parameters” of news and political ideas and whose authority as media commissars is challenged by the revolution of the internet.
The prize-winning former Guardian journalist Jonathan Cook has experience in both worlds.”The media, at least the supposedly left-wing component of it,” he writes, “should be cheering on this revolution… And yet, mostly they are trying to co-opt, tame or subvert it [even] to discredit and ridicule the harbingers of the new age… Some of [campaign against Assange] clearly reflects a clash of personalities and egos, but it also looks suspiciously like the feud derives from a more profound ideological struggle [about] how information should be controlled a generation hence [and] the gatekeepers maintaining their control.”